Introduction
Oman is experiencing a transformative journey in its economic development, and at the heart of this progress lies the growing role of big data. In today’s fast-paced, digital-first world, data is not simply information; it is a vital resource that shapes policies, guides businesses, and strengthens national planning. For a country like Oman, which is actively diversifying its economy beyond oil and gas, big data has emerged as a powerful tool to achieve sustainable growth, innovation, and inclusivity. The ability to capture, analyze, and utilize data effectively ensures that decisions are not based on guesswork but on precise, real-time insights that reflect the changing needs of society.
Big Data as a Strategic Resource
The idea of treating data as an asset is relatively new in Oman, but its importance is undeniable. Big data goes beyond traditional statistics it includes information generated from social media, financial transactions, transportation systems, mobile devices, and even weather sensors. This large-scale information, when analyzed correctly, reveals patterns and trends that decision-makers might otherwise miss. For economic planning, big data provides clarity in understanding market demand, workforce requirements, consumer behaviors, and environmental challenges.
Oman recognizes that data is not just about numbers; it represents opportunities, risks, and insights that are critical for policy formulation. By positioning big data at the core of its economic strategy, the country can accelerate decision-making and implement solutions that directly align with the realities of its people and industries.
Enhancing Vision 2040 Through Data
Oman Vision 2040 is the country’s long-term blueprint to diversify its economy, promote innovation, and ensure a high quality of life for its citizens. Big data plays a central role in supporting this vision. Through advanced analytics, policymakers can measure progress against targets, identify sectors with the greatest growth potential, and respond quickly to economic fluctuations.
For example, data can help determine how tourism trends are evolving, what kind of renewable energy investments are most viable, and how the labor market is adapting to technological shifts. It also allows the government to evaluate the success of initiatives in education, healthcare, and entrepreneurship, ensuring resources are allocated to areas where they will have the most significant impact.

Data-Driven Policy Making
Traditional policymaking often relied on historical data and projections that were updated slowly. Big data, however, introduces speed and precision into this process. With continuous streams of information, policymakers can adjust strategies in real time. If a sudden change occurs in global oil prices, for instance, big data analytics can help Oman’s leaders evaluate the immediate impact on its economy and design countermeasures quickly.
Moreover, big data enables predictive modeling. By analyzing trends, the government can anticipate potential challenges, such as employment shifts due to automation or the economic effects of climate change, and prepare proactive strategies. This forward-looking approach ensures that policies are not just reactive but also resilient.
Empowering Key Sectors of the Economy
Oman’s economy is built on multiple pillars, and each can benefit from the application of big data.
Oil and Gas
While diversification is a priority, the oil and gas sector still remains vital. Big data analytics helps optimize exploration, production, and distribution. Predictive maintenance powered by data reduces downtime in machinery and improves safety, while market analysis ensures that exports are aligned with global demand trends.
Tourism
Tourism is a rising star in Oman’s diversification agenda. Big data enables a deep understanding of visitor behaviors, preferences, and spending patterns. By analyzing travel data, Oman can design more targeted tourism campaigns, improve services, and enhance visitor satisfaction. This leads to higher returns on investment in infrastructure and hospitality.
Logistics
Positioned strategically between Asia, Africa, and Europe, Oman aims to be a logistics hub. Big data enhances supply chain efficiency by predicting demand, optimizing routes, and minimizing delays at ports and customs. The integration of data ensures smooth trade operations and strengthens Oman’s global competitiveness.
Agriculture and Fisheries
Food security is an essential part of economic planning. Big data assists in monitoring crop yields, analyzing soil conditions, predicting weather patterns, and tracking fish stocks. These insights support sustainable farming and fishing practices, boosting productivity while protecting natural resources.
Finance and Banking
The financial sector thrives on data. Big data analytics improves risk management, enhances fraud detection, and helps banks design products tailored to customer needs. For Oman, this translates into a more resilient financial system that supports entrepreneurship and consumer trust.
Big Data and Human Capital Development
Economic growth is not only about industries; it is about people. In Oman, big data is being used to better understand workforce dynamics and educational needs. By analyzing labor market data, the government can identify skill gaps and design training programs that prepare citizens for future jobs.
Education systems can also use data to personalize learning experiences, track student progress, and ensure alignment with national development goals. This data-driven approach helps create a workforce that is adaptable, skilled, and ready to meet the challenges of a knowledge-based economy.
Supporting Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
SMEs are the backbone of any economy, and Oman is no exception. Big data offers smaller businesses the ability to compete effectively by providing market intelligence, customer insights, and performance analytics. Access to such information allows SMEs to make better decisions, reduce risks, and innovate with confidence.
When government agencies use big data to identify emerging industries, they can create policies that directly support SMEs operating in those fields. This synergy accelerates growth, fosters entrepreneurship, and builds a more diverse economy.
Digital Infrastructure as a Foundation
To harness the potential of big data, strong digital infrastructure is essential. Oman has been investing in expanding broadband connectivity, data centers, and cloud platforms to support its digital transformation. Without robust infrastructure, data cannot flow seamlessly between organizations, industries, and government agencies.
Cloud computing and advanced storage systems ensure that Oman can handle the vast amount of data being generated daily. Simultaneously, investments in cybersecurity protect this data from breaches and misuse, ensuring trust among citizens and businesses.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Analytics
Big data alone is not enough it needs intelligent systems to process and interpret it. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning enhance Oman’s ability to extract meaningful insights from massive datasets. From predictive analytics in healthcare to smart city planning, AI ensures that the value of data is fully realized.
In economic planning, AI models can analyze consumer behaviors, predict future trends, and optimize decision-making across multiple sectors. This fusion of big data and AI ensures that Oman remains agile and competitive in a rapidly changing global economy.
Sustainability and Environmental Insights
Oman’s natural environment is a cornerstone of its identity, and sustainability is a key focus of economic planning. Big data supports environmental protection by monitoring air quality, tracking energy consumption, and studying the impact of industrial activity on ecosystems.
With climate change presenting new challenges, data-driven strategies are essential for adapting agriculture, conserving water resources, and expanding renewable energy projects. These insights allow Oman to balance economic growth with ecological responsibility.
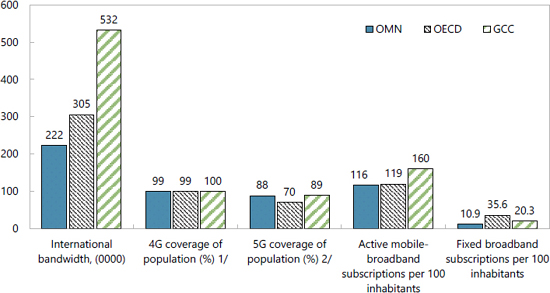
Public Services and Citizen Wellbeing
Economic planning is not only about GDP growth; it is also about enhancing quality of life. Big data strengthens healthcare by enabling predictive diagnostics, monitoring disease outbreaks, and personalizing patient care. In education, it helps design curricula that reflect the needs of both students and the labor market.
Smart governance also ensures efficiency in public services. By analyzing traffic data, Oman can reduce congestion in cities. By studying social service usage, the government can design welfare programs that truly address citizens’ needs. These applications build trust and foster a stronger connection between government and society.
Challenges in Implementing Big Data
While the potential is enormous, Oman faces challenges in adopting big data fully. These include the need for skilled professionals, the cost of advanced technologies, and concerns around privacy and security. Building a strong culture of data literacy is essential, so citizens and organizations can appreciate the benefits of data-driven decisions.
Moreover, collaboration between government, private sector, and academia is vital. Without sharing data responsibly across institutions, the full power of big data cannot be realized. Addressing these challenges requires investment, training, and policies that promote innovation while safeguarding citizens’ rights.
Building a Data-Driven Future
Despite challenges, the momentum toward a data-driven economy in Oman is clear. By encouraging innovation, investing in infrastructure, and fostering collaboration, Oman can unlock the full potential of big data. The benefits extend beyond economics big data strengthens resilience, inclusivity, and sustainability.
The path ahead involves not only technology but also mindset. A culture that values data, encourages curiosity, and embraces change will ensure that big data becomes a tool of empowerment for all Omanis.
Conclusion
Big data is no longer a luxury; it is a necessity for countries seeking to thrive in the modern era. For Oman, it provides a compass that guides economic planning with clarity, precision, and foresight. From enhancing key industries to shaping policies, from empowering individuals to supporting national vision, big data is at the heart of Oman’s transformation.
The journey may present challenges, but the rewards are immense. As Oman embraces the power of big data, it is not just building an economy it is building a future that is smart, sustainable, and inclusive for generations to come.
Also Read – Empowering Oman’s Future with Digital Identity Systems



