Lebanese President Joseph Aoun’s Landmark Visit to Saudi Arabia: A Step Towards ReconciliationDiabetes mellitus, particularly Type 2 diabetes (T2DM), has become a major public health concern in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA). Recent studies estimate that around 28% of the adult population is affected by this chronic condition. However, the prevalence of diabetes is not uniform across the country, with significant disparities between different regions. This growing health crisis highlights the urgent need for effective management strategies and public awareness campaigns to control its spread and impact.
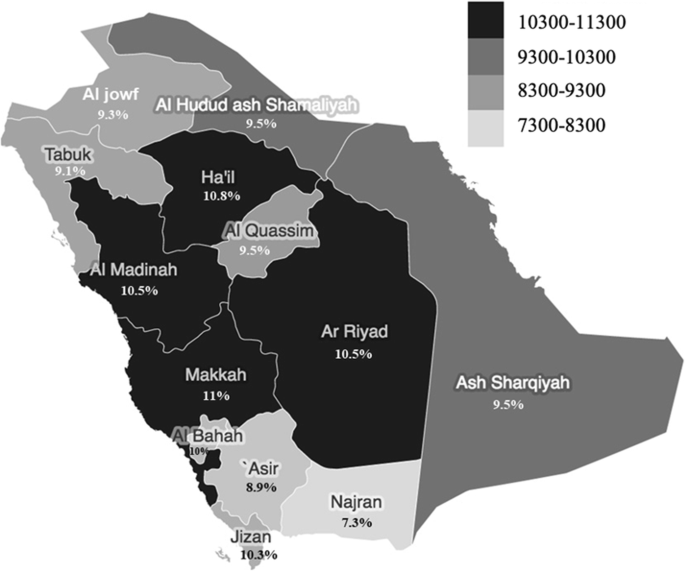
Regional Variations in Diabetes Prevalence
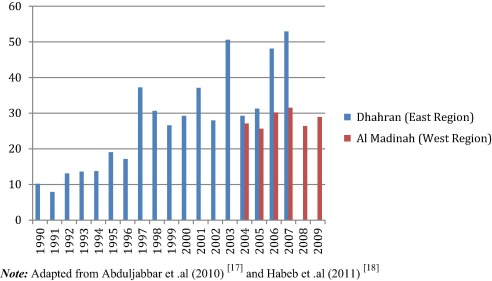
Saudi Arabia’s diverse geography and demographics contribute to significant variations in diabetes prevalence across its regions. Studies have shown that the northern, central, and southern regions exhibit the highest rates of uncontrolled diabetes, with less than 20% of patients achieving proper glycemic control. In contrast, the western and eastern regions demonstrate better management, with approximately 40% of patients maintaining controlled blood sugar levels.
These disparities can be attributed to a range of factors, including differences in healthcare infrastructure, socioeconomic status, lifestyle choices, and public health initiatives. Urban areas, particularly Riyadh, Jeddah, and Dammam, generally have better healthcare facilities and access to specialists, which contributes to more effective diabetes management. Meanwhile, rural regions often struggle with limited access to healthcare services, lower health literacy, and fewer resources for managing chronic diseases.
Key Factors Influencing Diabetes Rates in KSA
- Age and Demographics:
The risk of developing Type 2 diabetes increases significantly with age. Regions with a higher proportion of residents aged 40 and above tend to have higher prevalence rates. With a steadily aging population, Saudi Arabia faces a growing burden of diabetes, particularly among older adults. - Obesity and Sedentary Lifestyles:
Obesity is a major risk factor for diabetes, and Saudi Arabia has some of the highest obesity rates in the world. Sedentary lifestyles, driven by urbanization and a lack of public spaces for physical activity, exacerbate this problem. High-calorie diets rich in sugar and fats are also prevalent, further increasing the risk of diabetes. - Genetics and Family History:
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in the prevalence of diabetes in Saudi Arabia. A strong family history of diabetes is common, making early screening and preventive measures crucial for those at higher risk. - Healthcare Accessibility:
Access to healthcare services, particularly in remote areas, remains a challenge. While urban centers benefit from advanced medical facilities and specialists, rural regions often lack the infrastructure necessary for effective diabetes management.
Common Complications and Comorbidities
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to a range of serious complications and comorbidities. In Saudi Arabia, the most common complications among diabetes patients include:
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Heart disease and stroke are leading causes of mortality among diabetic patients in the Kingdom. Uncontrolled blood sugar levels contribute significantly to the risk of atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular conditions.
- Retinopathy: Diabetic retinopathy is a prevalent complication, leading to vision impairment and, in severe cases, blindness. Regular eye examinations and glycemic control are essential to prevent this condition.
- Kidney Disease: Diabetic nephropathy is a major cause of chronic kidney disease in Saudi Arabia. High blood sugar damages the kidneys’ filtering system, necessitating early intervention and management.
- Neuropathy: Peripheral neuropathy, causing numbness and pain in the extremities, is a common issue among long-term diabetes patients. Proper blood sugar management can help reduce the risk of nerve damage.
Current Management Strategies in Saudi Arabia
The management of diabetes in KSA involves a multi-faceted approach, combining medication, lifestyle modifications, and public health initiatives. Key management strategies include:
- Medications:
Metformin is the most commonly prescribed medication for Type 2 diabetes, followed by DPP-4 inhibitors and insulin therapy for more advanced cases. Newer classes of drugs, such as GLP-1 agonists and SGLT-2 inhibitors, are also being adopted for their effectiveness in glycemic control and cardiovascular benefits. - Lifestyle Modifications:
Public health campaigns emphasizing the importance of diet and exercise are gaining traction. Initiatives promoting walking, cycling, and healthier food choices aim to curb the rising tide of obesity and diabetes. - Healthcare Facilities and Training:
The Ministry of Health has been investing in specialized diabetes centers across the country, providing comprehensive care including regular monitoring, medication management, and patient education. Training healthcare professionals in the latest diabetes management guidelines is also a priority. - Awareness Campaigns:
National campaigns highlighting the risks of diabetes and the importance of early detection have been rolled out. Free screening camps and educational workshops are helping to improve public awareness, especially in high-risk communities.
Challenges in Diabetes Management
Despite these efforts, several challenges persist in managing diabetes effectively in Saudi Arabia:
- Patient Compliance:
A significant number of patients fail to adhere to prescribed medications and lifestyle changes, resulting in poor glycemic control. Cultural factors, lack of awareness, and misconceptions about insulin use contribute to this issue. - Healthcare Inequality:
Disparities in healthcare access between urban and rural areas hinder the effectiveness of national diabetes management strategies. Enhancing healthcare infrastructure in remote regions remains a critical need. - Economic Burden:
The cost of diabetes management, including medications, monitoring equipment, and treatment for complications, poses a significant economic burden on the healthcare system. Implementing cost-effective preventive measures could alleviate this pressure.
Future Directions and Recommendations
To combat the growing diabetes crisis, Saudi Arabia must adopt a comprehensive strategy focusing on prevention, early detection, and effective management. Key recommendations include:
- Enhanced Screening Programs: Regular nationwide screenings to identify pre-diabetes and undiagnosed diabetes cases can help initiate early intervention.
- Integrated Care Approach: Establishing a seamless referral system between primary care, specialists, and diabetes centers would improve patient outcomes.
- Focus on Youth and Prevention: Initiatives targeting younger populations, promoting physical activity, and addressing childhood obesity can help reduce future diabetes rates.
- Investment in Research: Supporting local research on diabetes and its complications can provide valuable insights for more targeted management strategies.
Conclusion
The rising prevalence of diabetes in Saudi Arabia, coupled with significant regional disparities, highlights the need for a coordinated national response. Effective management strategies, improved healthcare access, and public awareness are essential to curb this growing health crisis. By adopting a proactive approach focusing on prevention, early detection, and comprehensive care, Saudi Arabia can mitigate the impact of diabetes and ensure a healthier future for its citizens.
Lebanese President Joseph Aoun’s Landmark Visit to Saudi Arabia: A Step Towards Reconciliation