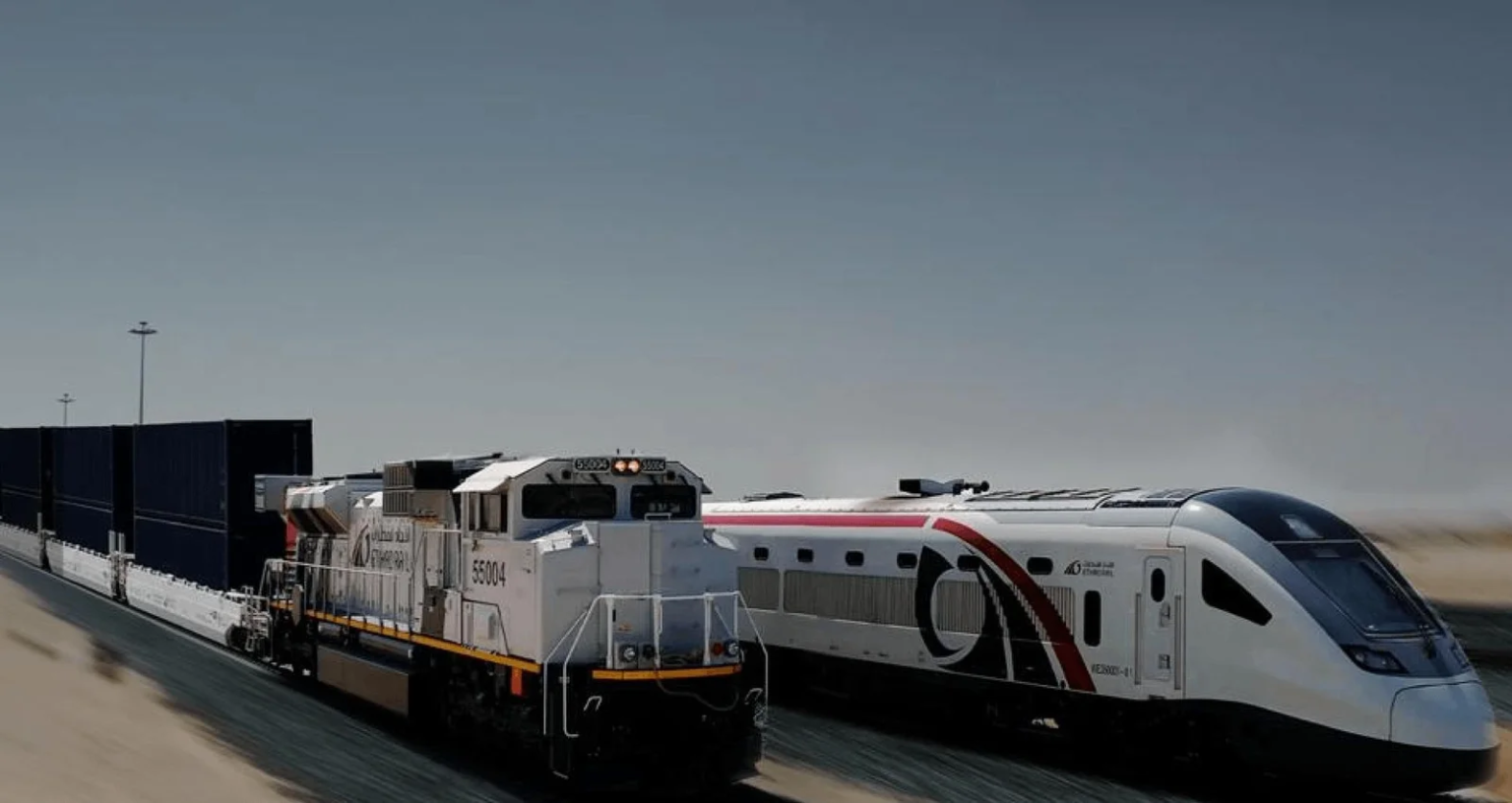
Riyadh / Abu Dhabi / Doha — The Gulf Railway Project, a landmark initiative to connect all six Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries by rail, is rapidly gaining momentum. With a planned completion by 2030, this ambitious regional railway aims to revolutionize transportation, trade, and economic integration across the Gulf.
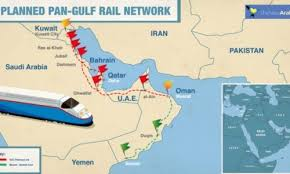
Once complete, the railway will link Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, Qatar, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), and Oman, covering more than 2,000 kilometers. It promises faster cargo movement, smoother passenger travel, and stronger economic ties in one of the world’s most strategically important regions.
What Is the Gulf Railway Project?
Also known as the GCC Railway, the project is a long-planned, multi-billion-dollar effort to build a modern rail network connecting all six member states. It will allow passenger and freight trains to move seamlessly across borders, reducing pressure on highways and improving logistics for businesses.

The idea was first introduced in the early 2000s, but serious steps toward implementation began in the past decade, driven by
- Rapid population growth
- Increasing trade volumes
- Environmental concerns
- A shared vision for GCC economic unity
Each country is responsible for building and financing the section of railway within its borders, with coordination from the GCC Secretariat General to ensure integration and uniform standards.
Project Timeline and Route Highlights
According to officials, the full Gulf Railway is expected to be operational by 2030, with some sections already under construction or in advanced planning stages. Key segments of the route include:
- Kuwait to Saudi Arabia: Connecting through the border town of Al Khafji.
- Saudi Arabia to Bahrain: Via the new King Hamad Causeway, alongside an existing road bridge.
- Saudi Arabia to Qatar: Crossing the Salwa border.
- UAE to Saudi Arabia: A key stretch linking Abu Dhabi and Riyadh.
- UAE to Oman: Connecting Al Ain to Sohar through the Hafeet border.
The UAE is already making fast progress. Its Etihad Rail project, part of the Gulf Railway, is in advanced phases, with freight services active and passenger services expected soon. Oman and Saudi Arabia signed a railway cooperation agreement in 2023, signaling growing commitment across the region.
Benefits: Why the Gulf Railway Matters
The Gulf Railway isn’t just a transportation project — it’s a strategic tool for economic and social transformation.
1. Boosting Regional Trade
Currently, most trade between GCC countries depends on trucks and sea routes. The railway will provide a faster, cheaper, and more sustainable alternative for moving goods.
“Rail freight can reduce delivery time by 30–40% and lower costs,” says a transport economist in Riyadh.
2. Connecting People Across Borders
The new passenger services will allow residents to travel from Kuwait to Muscat by train, with stops in major cities like Riyadh, Doha, and Abu Dhabi. This will support tourism, business travel, and cultural exchange.
3. Reducing Carbon Emissions
With growing pressure to cut carbon footprints, rail offers a cleaner option compared to cars or planes. Modern electric trains can reduce transport emissions and help meet net-zero targets.
4. Job Creation and Economic Growth
The construction, operation, and maintenance of the railway are expected to create thousands of jobs across the Gulf and stimulate investment in real estate, logistics, and industrial hubs along the route.
International and Regional Collaboration
The Gulf Railway Project is not just a domestic infrastructure plan — it is part of a larger regional vision for unity and cooperation. GCC leaders have repeatedly emphasized the importance of shared infrastructure in achieving long-term economic integration.
Several countries are collaborating with international engineering and construction firms from China, Europe, and the U.S., bringing world-class expertise and technology to the project.
“The railway is a physical symbol of GCC unity,” said a Gulf diplomat. “It sends a message that we are stronger together.”
Challenges Along the Track
While enthusiasm for the Gulf Railway is high, there are still challenges that could delay or complicate the project.
1. Funding and Costs
The total cost of the project is estimated to be around $250 billion, a major investment even for oil-rich states. Some delays in the past were due to budget constraints and shifting priorities.
2. Border and Customs Coordination
Smooth cross-border movement requires harmonized customs procedures and unified technical standards (such as gauge size, signaling, and safety systems). These need close coordination between governments.
3. Timeline Management
Each country is building its section independently, which means uneven progress can delay the overall project. Ensuring synchronized timelines is key to success.
Looking Ahead: A New Era for Gulf Mobility
Despite challenges, the Gulf Railway is on track to become a reality by 2030. With growing political support, rising trade, and ambitious national visions like Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 and the UAE’s Centennial 2071, the railway fits perfectly into the broader goal of a diversified, connected, and resilient Gulf economy.
Experts believe the project could later be linked with wider rail networks extending to Jordan, Iraq, Egypt, and even Asia and Europe, opening new trade corridors and boosting the Gulf’s global standing.
“This railway is not just for the Gulf — it’s a gateway to the world,” said a logistics CEO in Dubai.
Conclusion: Full Steam Ahead for Gulf Unity
The Gulf Railway Project is more than steel tracks and trains—it’s a symbol of a connected future. It reflects the region’s shared commitment to economic integration, sustainability, and innovation.
As construction picks up speed and cooperation deepens, the railway will play a major role in shaping the next chapter of GCC development—bringing countries, businesses, and people closer than ever before.
WATCH MORE LIKE THIS: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IgAvXMujHrk
READ MORE LIKE THIS:Eco-Friendly Buildings Rising Across GCC with Stunning Innovation



