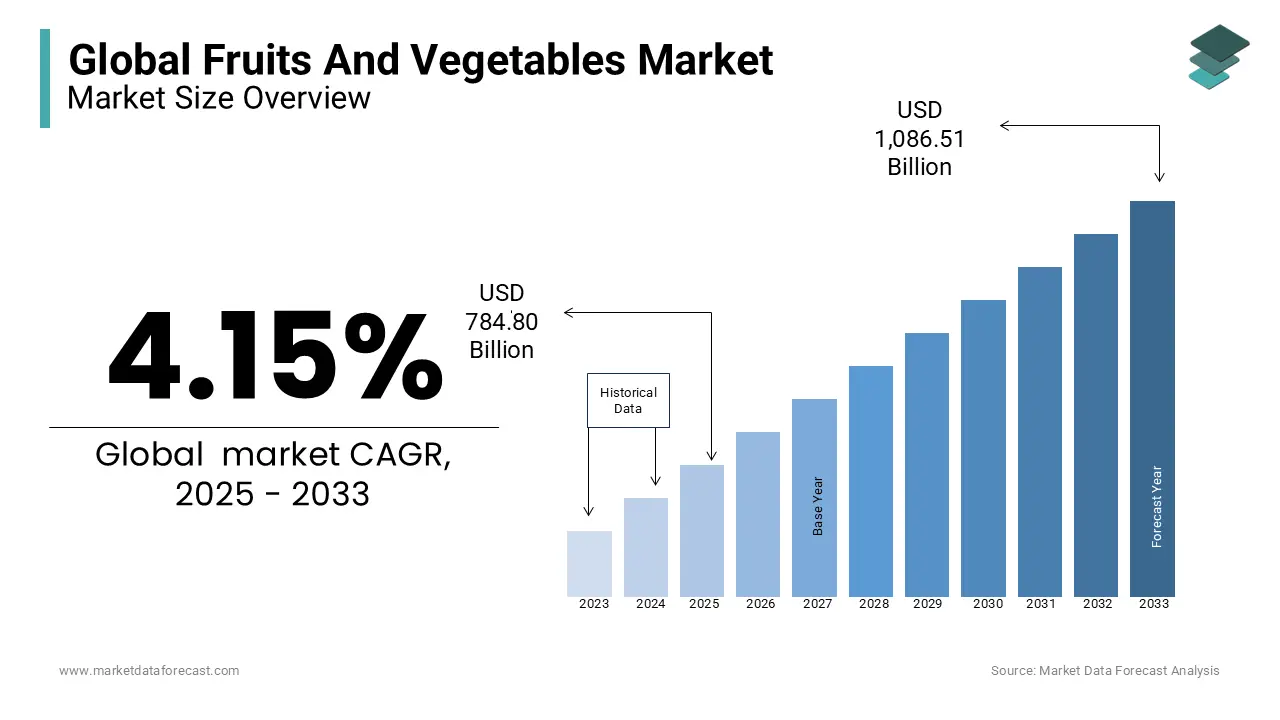
Kuwait’s Essential Food Imports may witness a significant drop of 20% by the year 2026, raising concerns across the region about food security, inflation, and availability of key daily necessities. With global trade tensions and shifting agricultural patterns playing a role, experts believe the country may need to rethink its import strategies and focus more on domestic production and diversification.
According to recent economic projections and trade analysis, Kuwait’s Essential Food Imports are expected to decline due to a combination of global supply disruptions, new local policies, and climate-related impacts in major exporting countries. This expected drop could affect essential staples such as rice, wheat, cooking oil, vegetables, and dairy—products that form the backbone of Kuwaiti households.
What’s Behind the 20% Drop?

The expected decline in Kuwait’s Essential Food Imports is not caused by a single factor. It is the result of a complex combination of global and regional challenges.
- Global Agricultural Stress
Major food-exporting countries are currently facing droughts, floods, and soil degradation. These climate challenges are reducing their ability to export at previous volumes. For example, India and Pakistan, two major exporters of rice and vegetables to Kuwait, are dealing with extreme weather events, resulting in reduced crop yields. - Shipping and Logistic Bottlenecks
The global shipping industry is still facing the ripple effects of post-pandemic disruptions. Rising freight costs, container shortages, and delays at ports have made it more expensive and unpredictable to import food. Kuwait, being heavily reliant on maritime imports, is directly affected by these challenges. - Policy Shifts in Kuwait
The government of Kuwait is also initiating new strategies to reduce overdependence on food imports. Recent investments in hydroponics, vertical farming, and local dairy production are aimed at improving food sustainability. While these are long-term solutions, they are influencing the overall import volume projections for 2026. - Currency Exchange Pressures
The strengthening of the US dollar and weakening of other global currencies are making imports more expensive for Kuwait. This leads to selective buying and reduced import volumes for non-essential or high-cost products.
Impact on Daily Life in Kuwait
For many residents in Kuwait, this expected decline in food imports could lead to noticeable changes at supermarkets and restaurants. Prices of certain imported goods may rise due to low supply, and availability might be limited for specific food items.
Imported rice, which is a staple in most Kuwaiti homes, could become more expensive. Vegetables like onions, tomatoes, and leafy greens that are mostly imported may see price hikes. Cooking oils and processed food items might also be stocked in smaller quantities.
Restaurants and catering businesses may be forced to revise their menus or increase prices due to rising food costs. Overall, consumers will likely feel the pinch in their wallets, even if the government steps in with subsidies or price controls.
Government Response and Food Security Measures

The Kuwaiti government has already taken a few steps to minimize the impact of this potential drop. The Ministry of Commerce and Industry is working on strategic food reserves to ensure supply stability. New collaborations with regional producers in the Middle East and North Africa are also in discussion.
In addition, several pilot programs have been launched to promote sustainable farming within Kuwait’s desert climate. Technologies such as hydroponics and aquaponics are gaining popularity as cost-effective and water-efficient solutions.
Authorities are also encouraging private sector investment in food production and distribution to reduce dependency on imports. Although these steps may take a few years to produce large-scale results, they represent a long-term commitment to food security.
The Road Ahead: Can Kuwait Avoid the Food Import Decline?
While the 20% forecast drop in Kuwait’s Essential Food Imports is worrying, it also offers an opportunity for the nation to accelerate its efforts toward food independence. By investing in smart agriculture and building local capacities, Kuwait can turn this challenge into a strategic advantage.
Public awareness is also key. Citizens and residents are being encouraged to reduce food waste, support local products, and adopt a more sustainable lifestyle. Educational campaigns and workshops are being organized to help consumers understand the importance of food security and how they can contribute.
Kuwait’s policymakers are expected to present a new National Food Strategy by early 2026. The strategy is likely to include diversified import partnerships, stronger food reserves, and an expansion of domestic agricultural projects.
Final Thoughts
The anticipated 20% decline in Kuwait’s Essential Food Imports by 2026 is not just a trade issue—it is a social, economic, and environmental matter. If not managed carefully, it could lead to inflation, shortages, and unrest. However, with the right planning, investment, and innovation, Kuwait can use this moment to build a stronger, more self-reliant food system.
Residents are advised to stay informed and support the shift toward sustainable consumption. Meanwhile, the private and public sectors must work together to ensure that every Kuwaiti household has access to affordable and essential food products in the years to come.
Also Read – Worst Food Safety Mistakes Restaurants Make in Kuwait