Modern cities around the world are grappling with energy waste, spiralling demand, and environmental concerns but Kuwait stands out as a nation ready to embrace the future. In this article, we explore how machine learning (ML) is being wielded to transform the country’s energy consumption patterns, making life greener, smarter, and more efficient for businesses and families alike.
The energy challenge in Kuwait
Kuwait, with its thriving economy and rapidly growing population, has seen rising energy demands across residential, industrial, and commercial sectors. The nation’s desert climate pushes air conditioning systems into overdrive, creating extreme peaks in electricity usage. At the same time, reliance on oil and gas means missed opportunities for optimising energy distribution and reducing waste. The traditional utility systems are not dynamic enough to respond in real time, resulting in avoidable inefficiencies and high operational costs.
What machine learning brings to the table
Machine learning, as a branch of artificial intelligence, offers the ability to process vast datasets, find hidden patterns, and predict future behaviour. In the energy sector, ML tools can analyse consumption trends, forecast demand, optimise grid operations, and recommend personalised energy saving measures. Using sensors, smart meters, and historical data, ML models can respond quickly to shifting conditions, maximising efficiency and reducing wastage.
Forecasting demand accurately
A core application of ML in Kuwait involves predicting electricity demand hours or days in advance. By feeding models data such as temperature, humidity, time of day, historical usage, and even social events, energy providers can precisely estimate when demand will spike. This enables utilities to prepare generation capacity and avoid costly last minute ramp ups. It also helps minimize blackouts and ensures a reliable electricity supply for all regions.
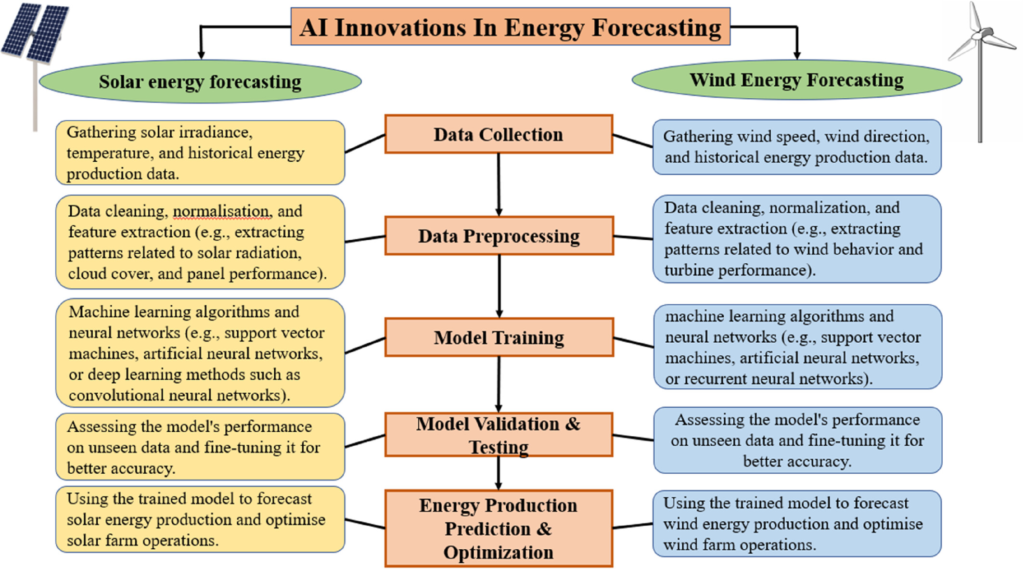
Dynamic pricing for smarter consumption
Machine learning systems can enable dynamic pricing schemes, where electricity prices fluctuate with real time demand. Consumers receive signals such as lower rates during low usage periods, encouraging them to shift consumption (for example, cooling or running washers at night). Households and businesses become participants in grid balancing, lowering peak loads. Over time, this creates more even energy use curves, reduces the strain on infrastructure, and results in lower bills for proactive users.
Optimizing air conditioning systems
Since air conditioning makes up a massive portion of Kuwait’s residential and commercial energy consumption, ML offers huge potential here. Smart thermostats and building automation systems learn from usage patterns and environmental data. They fine tune the temperature, airflow, and system cycles to deliver comfort with minimal energy. In large commercial buildings, ML can coordinate multiple HVAC units to avoid overlap and redundancy. The result: substantial energy savings coupled with consistent indoor comfort.
Grid load balancing and renewable integration
As Kuwait explores renewable energy sources like solar and wind, machine learning plays a pivotal role in managing variability. ML algorithms forecast renewable generation output and adjust conventional power generation accordingly. They also detect grid anomalies or potential instabilities. By balancing loads and integrating renewable intelligently, ML helps reduce over dependence on fossil fuels and increases grid resilience, paving the way for a cleaner, more sustainable energy infrastructure.
Energy audits powered by AI
Conducting audits across homes, factories, and public buildings can reveal hidden inefficiencies: outdated equipment, poor insulation, or outdated practices. Machine learning streamlines these audits by analysing consumption data and pointing to areas of waste. Simple dashboards provide clear recommendations: upgrade equipment, seal leaks, tune machinery, or adjust routines. Consumers receive actionable insights, and energy auditors can prioritise high impact improvements, accelerating savings across sectors.

Empowering consumers with personalized feedback
People respond better when they understand their impact. Machine learning based apps can offer households personalised feedback, daily energy summaries, comparisons to neighbours, tailored tips to reduce consumption. Gamification elements, like friendly challenges or rewards for energy saving, increase engagement. Over time, these habits ripple across communities: small daily actions add up to major reductions in energy use nationwide.
Industrial efficiency gains
Industries in Kuwait petrochemicals, manufacturing, water desalination consume massive energy loads. ML can monitor machinery, forecast maintenance, and optimise production cycles. Predictive maintenance models flag under performing equipment, reducing downtime and energy waste. Optimisation tools suggest how to run processes at the most efficient settings. The result: lower operational costs, improved productivity, and a more sustainable industrial sector.
Government policy and regulatory support
For machine learning to truly transform Kuwait’s energy consumption, government support is key. Policies encouraging data driven efficiency, incentives for smart grid investments, and regulations around demand response programs help accelerate adoption. Clear guidelines around data privacy and cybersecurity build consumer trust. When energy providers collaborate with regulators, innovative ML systems can scale rapidly, benefiting businesses, citizens, and the overall economy.
Building partnerships and local expertise
International technology firms bring powerful ML solutions, but local partners bring contextual know how. Collaborations between universities, startups, and energy companies foster tailored ML products for Kuwait’s climate and infrastructure. Training local talent in data science and AI makes Kuwait less dependent on foreign suppliers. These partnerships also drive innovation, helping the nation pioneer home grown solutions that could scale regionally.
Real world success stories
Several pilot projects in Middle East countries show what’s possible. Smart meter deployments in residential communities achieved double digit reductions in peak energy demand. Commercial buildings equipped with AI driven HVAC controls saw dramatic drops in monthly electricity bills while tenant comfort improved. Such experiences raise excitement in Kuwait’s utility sector: imagine stretching those benefits across the country’s neighbourhoods, businesses, and industrial zones.
Challenges to overcome
Nothing trans formative comes without hurdles. High quality data is essential for accurate ML models, but legacy systems may lack robust recording. Integrating sensors, meters, and platforms requires upfront investment. Cybersecurity is a constant concern: as grids become smarter, the risk of digital attacks increases. Finally, changing consumer behaviour encouraging people to respond to dynamic pricing or feedback depends on awareness campaigns and easy to use tools. Overcoming these challenges requires clear planning, investment, and a culture shift toward efficiency.
Measuring impact cost savings and carbon reductions
When deployed well, ML driven energy optimisation can deliver measurable impact. Utilities can reduce peak generation costs by shifting demand. Households and businesses see lower monthly bills. On a national scale, optimised consumption lowers overall energy output and cuts CO₂ emissions. Kuwait’s oil reserves can go further if internal consumption is reduced, leaving more for export or future generations. For citizens and policymakers, the benefits are both economic and environmental.
A human centred technology
While the math behind machine learning is complex, the end result is about people families who pay less for air conditioning, workers in offices that stay cool without waste, industries that produce more with less power. It is also about children growing up in a cleaner environment and a country building a sustainable future. When consumers interact with simple dashboards, receive helpful suggestions, and see real results, they feel empowered. That trust in technology fuels further adoption and innovation.
Next steps for Kuwait
To unlock these gains, Kuwait can follow a clear roadmap:
- Deploy smart meters widely across neighborhoods and commercial zones
- Roll out pilot programs in selected buildings to test HVAC optimization and predictive maintenance
- Incentivize utilities to adopt dynamic pricing and demand response programs
- Invest in local data science capacity through universities and training institutes
- Launch public awareness campaigns that show people how to save energy with new tools
- Ensure robust cybersecurity and transparent data practices to build trust
Each of these steps builds momentum, combining technological innovation with real life impact.
Looking ahead a smarter, greener Kuwait
Over time, machine learning’s role in Kuwait’s energy landscape can expand: smart grids that self balance, homes that learn and adapt to occupants, industries that run with minimal waste, and national planning powered by accurate forecasting. As these systems mature, the nation can reduce fossil fuel dependency, lower domestic emissions, and secure energy for generations. Ultimately, the transformation is not just about machines, it is about smarter decisions, empowered people, and a more sustainable future.
Conclusion
Machine learning offers Kuwait a powerful path to optimise its energy consumption patterns. By forecasting demand, enabling dynamic pricing, optimising HVAC and industrial systems, and empowering consumers with data driven insights, ML can reduce waste, cut costs, and enhance comfort. While challenges remain data quality, cybersecurity, behavioural change the potential payoff is real: a greener, smarter Kuwait built on human centred technology. With policy support, local collaboration, and public buy in, this vision is not just possible, it is within reach.
Do follow Gulf Magazine on Instagram.
Also Read – Biotechnology Research Hubs in Qatar Driving Groundbreaking Scientific Discoveries



