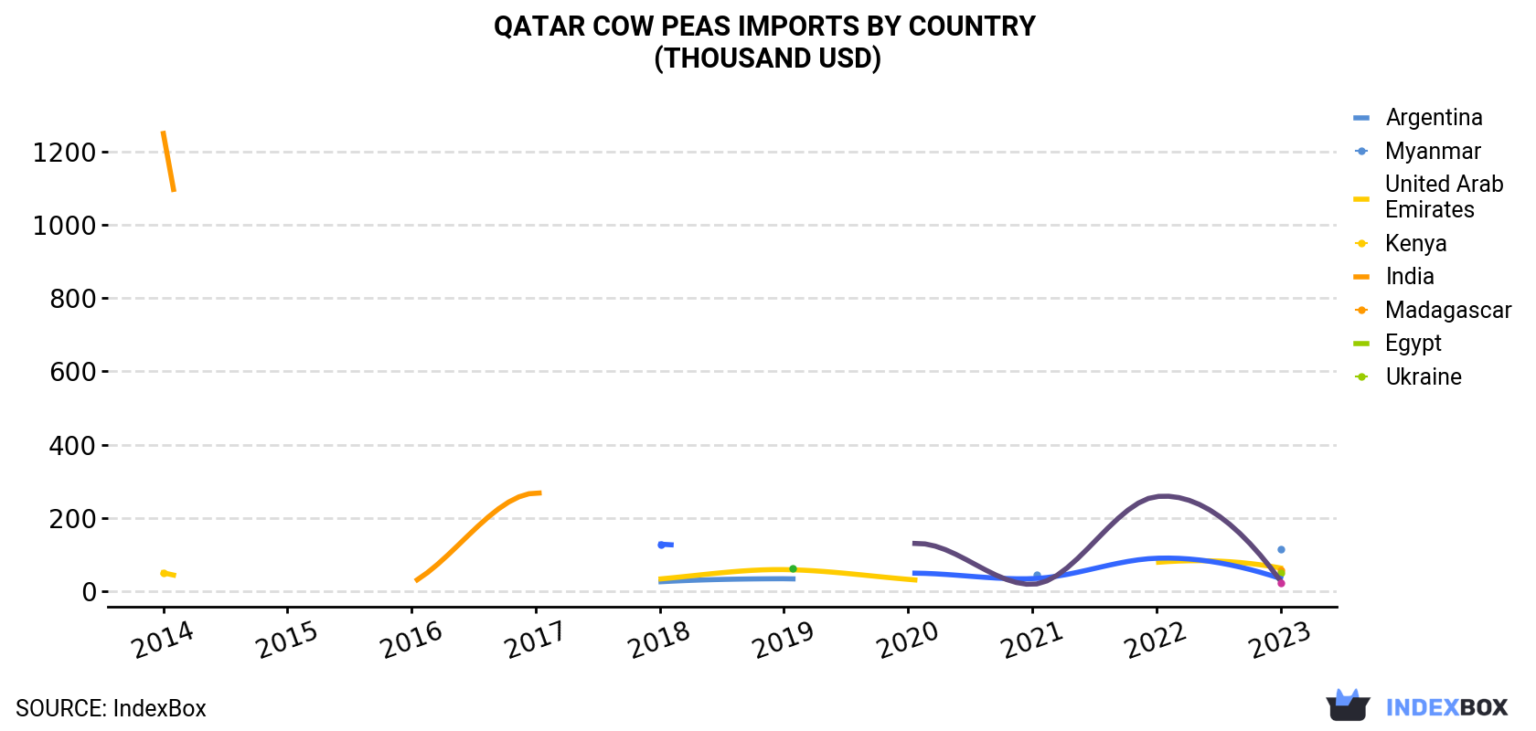
In 2022, Qatar witnessed a substantial reduction in its cow peas imports, marking a 63.5% decrease to just 200 tons. This downturn came after three consecutive years of growth, signaling a significant shift in the country’s import trends. Despite the previous surge in demand, Qatar’s reliance on cow peas imports declined dramatically, prompting industry analysts to examine the factors behind this sudden drop and its potential long-term effects on the market.
Cow peas, also known as black-eyed peas, are widely consumed in many parts of the world, including the Middle East. They are a vital ingredient in many traditional dishes and are valued for their nutritional benefits, including high protein and fiber content. The demand for cow peas in Qatar had been growing steadily in recent years, reaching its peak in 2020, when imports surged by an astonishing 400%. However, this rapid increase was followed by a significant contraction, raising questions about changes in consumer preferences, market conditions, and supply chain disruptions.
The Downward Trend in Import Volume and Value

The sharp decline in cow peas imports in 2022 resulted in a substantial decrease in the overall market value. In monetary terms, Qatar’s cow peas imports fell to $217,000, a sharp drop compared to previous years. The peak of the import boom in 2020 saw a staggering 554% increase in the total value of imported cow peas. This drastic fluctuation suggests that Qatar’s market for cow peas is highly volatile and subject to various external and internal pressures.
The decrease in import volume and value may be attributed to multiple factors, including shifting dietary habits, supply chain challenges, and economic conditions. The global agricultural market has been experiencing significant disruptions due to rising transportation costs, changing trade policies, and climatic conditions affecting crop yields. Additionally, Qatar’s increasing focus on local food production and alternative imports may have played a role in the decline of cow peas imports.
Leading Suppliers and Their Share in the Market
Despite the overall decline, certain countries remained Qatar’s primary suppliers of cow peas in 2022. India led the market, supplying 82.9 tons of cow peas, followed by Myanmar with 48.1 tons, Nigeria with 46.4 tons, and Madagascar contributing 22.9 tons. These four countries collectively accounted for the majority of Qatar’s imports, reflecting the strong trade relationships established over the years.
India’s dominance as the leading supplier of cow peas to Qatar can be attributed to its large-scale production and competitive pricing. The country has been a major exporter of pulses and legumes to the Middle East, catering to the dietary preferences of the region’s diverse population. Myanmar, Nigeria, and Madagascar have also been key players in the market, offering high-quality cow peas that meet the standards of Qatari consumers.
Market Dynamics and Possible Causes of the Decline
The steep decline in cow peas imports in 2022 raises several important questions about market dynamics. One of the key factors influencing the downturn is the shift in Qatar’s import policies and food security strategies. In recent years, the country has been focusing on boosting domestic agricultural production and diversifying its food sources to reduce dependence on imports. This strategy may have led to a reduction in demand for imported cow peas.
Additionally, global supply chain disruptions have played a role in reducing import volumes. The COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on international trade, causing logistical challenges, increased shipping costs, and delays in supply chains. These disruptions may have discouraged importers from sourcing large quantities of cow peas, contributing to the decline in imports.
Another factor to consider is the fluctuating demand for cow peas in Qatar. Consumer preferences have been evolving, with more people shifting towards other types of legumes and plant-based proteins. The rise in popularity of alternative protein sources, such as lentils, chickpeas, and quinoa, could have reduced the demand for cow peas in the Qatari market.
Import Price Trends and Their Impact
The price of imported cow peas has been on an upward trend over the past five years, further influencing the decline in imports. In 2018, the average import price per kilogram of cow peas was $2.45, which increased to $3.50 in 2022. The steady rise in import prices can be attributed to factors such as higher production costs, transportation expenses, and inflationary pressures in the global market.
Higher import prices may have led to reduced purchasing power among consumers and businesses in Qatar, prompting them to seek more affordable alternatives. With price-sensitive markets, any significant increase in import costs can result in decreased demand and shifts in consumer behavior.
Comparison with Other Legumes
While cow peas imports declined, other legumes have shown different trends in the Qatari market. For instance, green peas imports surged by 60% in 2023, reaching a value of approximately $497,000. The primary suppliers of green peas to Qatar include Kenya, India, and Pakistan. This contrast suggests that Qatari consumers and businesses may be diversifying their legume consumption, opting for other varieties based on availability, affordability, and nutritional value.
The increasing preference for green peas and other legumes indicates a potential market shift, where cow peas are being replaced or supplemented with other pulse crops. This trend highlights the importance of staying updated on market preferences and adapting import strategies accordingly.
Future Outlook and Market Projections
Looking ahead, Qatar’s cow peas market is expected to remain dynamic, influenced by various economic, political, and consumer-driven factors. The sharp decline in imports in 2022 may be a temporary fluctuation, or it could signify a long-term trend towards reduced dependency on cow peas.
To ensure market stability, importers and stakeholders should closely monitor changes in demand, global trade policies, and agricultural production trends. Investing in alternative sources of legumes, improving domestic food production, and maintaining trade partnerships with key suppliers can help Qatar navigate potential future disruptions.
The government’s focus on food security and sustainable agriculture will likely play a crucial role in shaping future import trends. Policies that encourage local farming and reduce import reliance may further impact cow peas imports. However, if consumer demand rebounds, the market could experience a resurgence in imports, bringing new opportunities for suppliers and distributors.
Conclusion
Qatar’s cow peas imports faced a steep decline in 2022, reversing years of steady growth. This drop was influenced by multiple factors, including shifts in import policies, global supply chain disruptions, and changing consumer preferences. While India, Myanmar, Nigeria, and Madagascar remained key suppliers, the overall market experienced a downturn, leading to reduced import volumes and values.
The rising cost of imports, competition from other legumes, and Qatar’s food security initiatives further shaped the market landscape. Looking forward, stakeholders in the cow peas trade must adapt to these evolving trends to ensure stability and growth in the coming years.
As Qatar continues to develop its agricultural sector and diversify its food sources, the future of cow peas imports remains uncertain. However, by staying informed and responsive to market changes, businesses and policymakers can navigate the challenges and opportunities ahead in the evolving landscape of agricultural imports.