The Singapore-India-Gulf Subsea Cable is emerging as one of the most ambitious digital infrastructure projects connecting Asia and the Middle East. As global demand for data explodes—driven by cloud computing, AI, streaming, fintech, and e-commerce—countries and telecom giants are racing to build faster, more reliable internet highways beneath the sea. Among the companies taking a major stake in this project is UAE telecom operator du, which sees the cable as a cornerstone of its future growth.
But why is du investing heavily in this undersea network? What strategic advantages does it bring to the United Arab Emirates and the wider region? And how could it reshape global digital connectivity between Asia, the Gulf, and beyond?
This article explores the significance of the Singapore-India-Gulf Subsea Cable, du’s motivations, and the broader economic and geopolitical implications.
What Is the Singapore-India-Gulf Subsea Cable?
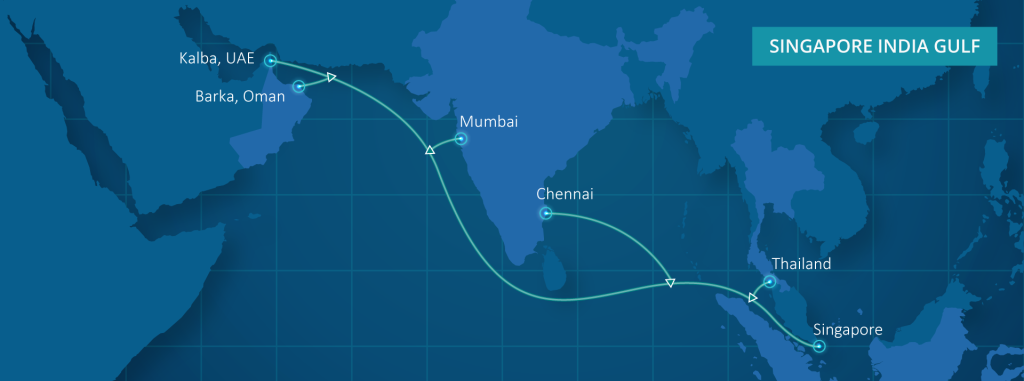
The Singapore-India-Gulf Subsea Cable is a high-capacity fiber-optic system designed to connect Singapore, India, and Gulf nations including the United Arab Emirates. Running along the seabed across thousands of kilometers, the cable will transmit massive volumes of data at ultra-high speeds.
Subsea cables form the backbone of the internet. Contrary to popular belief, satellites carry only a small portion of global data traffic. Over 95% of international internet traffic travels through undersea fiber-optic cables.
Key goals of the project include:
- Increasing bandwidth between Asia and the Middle East
- Reducing latency (data travel time)
- Improving reliability and redundancy
- Supporting cloud and AI infrastructure
- Strengthening digital trade routes
In simple terms, the cable will function as a digital superhighway linking some of the world’s fastest-growing economies.
Why the Project Matters Now
Global internet usage has surged dramatically in recent years. Video streaming, online gaming, remote work, smart devices, and artificial intelligence systems all demand enormous data capacity.
At the same time, governments in Asia and the Gulf are investing heavily in digital transformation. Cities are becoming “smart,” financial systems are moving online, and industries rely on real-time data exchange.
Existing cable networks are approaching capacity limits in certain corridors. Any disruption—whether from natural disasters, ship anchors, or geopolitical tensions—can slow internet speeds across entire regions.
The Singapore-India-Gulf Subsea Cable addresses these risks by:
- Adding new routes to reduce congestion
- Providing backup connectivity if other cables fail
- Enabling future technologies that require ultra-low latency
For countries positioning themselves as digital hubs, such infrastructure is essential.
Why du Is Betting Big on the Singapore-India-Gulf Subsea Cable
1. Transforming the UAE into a Global Digital Hub
The UAE aims to become a leading center for technology, finance, and innovation. High-capacity international connectivity is a key requirement for that vision.
By investing in the Singapore-India-Gulf Subsea Cable, du strengthens the country’s role as a bridge between East and West. Data traveling from Asia to Europe or Africa can pass through the Gulf, generating revenue and strategic importance.
This aligns with the UAE’s broader ambitions to diversify its economy beyond oil and position itself at the center of the digital economy.
2. Explosive Growth in Data Demand
Data consumption in the Gulf region is rising rapidly due to:
- 5G expansion
- Cloud computing adoption
- Streaming services
- Online education and healthcare
- AI development
Enterprises increasingly rely on international data exchange with partners in Asia, especially India and Southeast Asia.
A direct, high-capacity cable route ensures faster speeds and improved service quality for customers. For du, this translates into stronger competitiveness against regional telecom operators.
3. Strengthening Business and Enterprise Services
Telecom companies no longer rely solely on mobile subscribers. Enterprise connectivity, cloud hosting, and managed services are major revenue drivers.
Multinational corporations operating in the UAE need reliable connections to offices and data centers in Asia. Financial institutions, for example, depend on ultra-low latency networks for trading operations.
The Singapore-India-Gulf Subsea Cable enables du to offer premium services such as:
- Dedicated international bandwidth
- Secure data transmission
- Disaster recovery solutions
- Cloud interconnection
These services command higher margins than traditional telecom offerings.
4. Supporting Hyperscale Data Centers
Global technology companies are building massive data centers across the Middle East. These facilities store and process data for cloud platforms, AI models, and digital services.
However, data centers are only as effective as their connectivity. High-capacity subsea cables are essential to move data between regions efficiently.
By participating in the new cable system, du positions itself as a preferred connectivity partner for hyperscalers entering the Gulf market.
5. Enhancing Network Resilience
Internet outages can cause enormous economic losses. Redundancy—having multiple independent routes—is critical for national infrastructure.
If one cable is damaged, traffic can be rerouted through another. The Singapore-India-Gulf Subsea Cable provides an additional pathway, reducing the risk of widespread disruption.
For governments and businesses alike, resilience is as important as speed.
Strategic Importance of India in the Cable Route
India plays a central role in the project. As one of the world’s largest internet markets, it generates vast data flows to and from the Middle East.
Millions of expatriates from India live and work in Gulf countries, creating strong communication ties. Financial transactions, remittances, entertainment streaming, and business operations all depend on reliable connectivity.
India is also emerging as a major hub for software development, IT services, and digital startups. Faster links between India and the Gulf can stimulate trade, innovation, and investment.
Singapore’s Role as an Asian Digital Gateway
Singapore is widely regarded as Southeast Asia’s premier technology hub. It hosts numerous data centers and serves as a landing point for many international cables.
By connecting to Singapore, the new system links the Gulf directly to the broader Asia-Pacific network, including countries like Indonesia, Malaysia, Japan, and Australia.
This enhances the UAE’s ability to access markets across the region and strengthens its position in global data flows.
Economic Benefits for the Gulf Region
Boosting Digital Economies
Faster connectivity enables the growth of digital industries such as:
- E-commerce
- Fintech
- Online media
- Remote services
- Artificial intelligence
These sectors are central to economic diversification strategies across Gulf countries.
Attracting Foreign Investment
International companies prefer locations with world-class infrastructure. Reliable high-speed connectivity makes the UAE more attractive for regional headquarters, research centers, and technology operations.
Supporting Smart Cities and Innovation
Smart city initiatives rely on real-time data from sensors, cameras, and connected devices. High-capacity networks ensure seamless operation of transportation systems, utilities, healthcare platforms, and public services.
Geopolitical and Strategic Implications
Subsea cables are not just commercial projects—they are strategic assets. Control over data routes can influence economic and political power.
Countries are increasingly seeking to diversify connectivity to avoid dependence on a single route or region. The Singapore-India-Gulf Subsea Cable provides an alternative pathway that strengthens digital sovereignty.
It also enhances cooperation between Asia and the Middle East, potentially reshaping global digital alliances.
Environmental and Technical Challenges
Building undersea cables is a complex undertaking. Engineers must navigate deep ocean trenches, seismic zones, coral ecosystems, and busy shipping lanes.
Key challenges include:
- Protecting marine life
- Avoiding fishing areas and anchor damage
- Ensuring long-term durability
- Managing extreme depths and pressures
Modern cables are designed to operate reliably for decades, but maintenance and monitoring remain critical.
Competition Among Global Cable Projects
The Singapore-India-Gulf Subsea Cable is part of a broader wave of infrastructure development. Technology companies, telecom operators, and governments worldwide are funding new systems to support future data demand.
Major tech giants are even building private cables to secure dedicated capacity for their cloud services.
For du, participating in a consortium project ensures access to capacity without bearing the entire financial burden alone.
How Consumers May Benefit
While the project is primarily aimed at large-scale connectivity, everyday users could also see improvements, including:
- Faster international internet speeds
- Lower latency for gaming and video calls
- More reliable streaming services
- Improved cloud performance
- Potentially lower data costs over time
As capacity increases, congestion decreases—leading to a smoother online experience.
Risks and Uncertainties
Despite its promise, the project faces potential risks:
- High construction costs
- Regulatory approvals across multiple countries
- Technical challenges during installation
- Market competition
- Geopolitical tensions affecting routes
However, the long-term demand for data connectivity makes such investments increasingly attractive.
du’s Long-Term Vision
For du, the Singapore-India-Gulf Subsea Cable is not just a network upgrade—it is a strategic move to redefine its role in the global telecom landscape.
The company aims to transition from a traditional telecom provider into a digital services powerhouse offering connectivity, cloud solutions, cybersecurity, and smart infrastructure support.
Participation in major international projects signals its ambition to compete on a global scale.
What This Means for the Future of Connectivity
The digital world is entering a new phase driven by artificial intelligence, automation, and immersive technologies. These innovations require massive data transfer speeds and near-instant communication across continents.
Subsea cables like this one will underpin:
- AI training and deployment
- Autonomous systems
- Virtual and augmented reality
- Cross-border digital services
- Global financial networks
As demand continues to grow, more such projects are likely to emerge.
Conclusion
The Singapore-India-Gulf Subsea Cable represents a pivotal step in strengthening digital links between Asia and the Middle East. By investing heavily in the project, du is positioning itself—and the UAE—as a central node in the global data economy.
The cable promises faster speeds, greater reliability, economic growth, and strategic advantages for participating countries. While challenges remain, the long-term benefits could be transformative.
In an era where data is often called the “new oil,” infrastructure that moves information quickly and securely is becoming one of the world’s most valuable assets. du’s bold bet on the Singapore-India-Gulf Subsea Cable suggests that the future of connectivity will run not through the sky—but deep beneath the ocean.
Do follow us: Instagram
Also Read – Oman-India CEPA Nearing, Promising Prosperous Bilateral Future



